
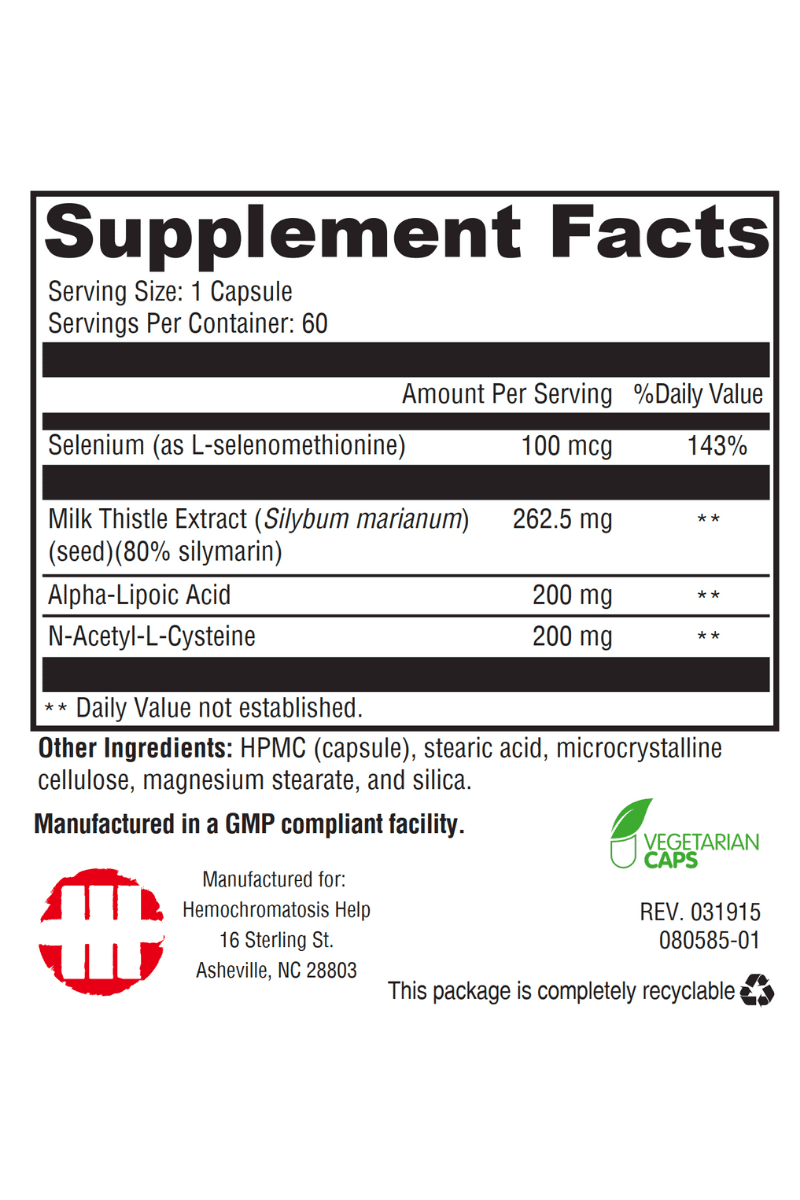

Hemochromatosis Help™ Milk Thistle Supreme
Highlights
- Milk Thistle blocks iron absorption and may reduce ferritin according to scientific research
- Classic herbal remedy to support liver health
- Synergistically combines 3 other powerful antioxidant nutrients:
- Alpha Lipoic Acid, N-Acetyl Cysteine, and Selenium
- Wide range of potential benefits to the health:
- Promotes glutathione production, supports a healthy metabolism, and helps to detoxify & eliminate toxins
- Also available as part of the Antioxidant, Essentials, Everything, & Supreme Bundles.
Health Benefits of Antioxidants in Hemochromatosis
Oxidation is a fundamental problem of hemochromatosis and a major reason why individuals develop health concerns over time.
Each ingredient in Hemochromatosis Help’s Milk Thistle Supreme supports the antioxidant functions of the body with a special affinity for supporting liver health, which is the organ most vulnerable to oxidative damage from iron overload.
Additionally, the remedies in Milk Thistle Supreme have been shown to help block the absorption of dietary iron and to even lower ferritin!
Why Milk Thistle Supreme?
Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum) is a favorite among herbalists for its strong hepatoprotective properties that support liver function and protect the body against toxins.
Powerful polyphenols found in Milk Thistle include Silymarin and Silybin, and these flavonoid compounds have been shown to benefit liver function and improve health. In particular, Silybin has been investigated in clinical research involving people with Hemochromatosis.
Specifically, Milk Thistle has been demonstrated to reduce iron absorption (which is exactly what we need!):
“In conclusion, silybin has the potential to reduce iron absorption, and this deserves further investigation, as silybin could be an adjunct in the treatment of haemochromatosis.” - Eur J Clin Nutr. 2010 Oct;64(10):1239-41.
Furthermore, another exciting benefit is Milk Thistle may help to reduce Ferritin:
“There was a significant decrease in serum ferritin from baseline to end of treatment… 78% of subjects had a decrease in serum ferritin level.” - J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008;42(8):937-944.



Alpha Lipoic Acid, N-Acetyl Cysteine, and Selenium:
Three Additional Powerful Antioxidants for Hemochromatosis
Milk Thistle Supreme contains three other key ingredients with well-established links to liver health.
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid (ALA): Plays a key role in removing toxins as well as being a powerful antioxidant that helps support other antioxidants.
- N-Acetyl-Cysteine (NAC): A precursor to glutathione, the chief antioxidant in the body, NAC is well documented to support liver health.
- Selenium: This mineral supports the health of liver cells by helping regulate inflammation and cellular structure.
ALA, NAC, and Selenium possess strong antioxidant properties on their own and help to regenerate the body’s natural antioxidant stores, including the most important antioxidant in the body, glutathione.
Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA)
Clinical research very strongly supports Alpha Lipoic Acid as a potent antioxidant. Additionally, multiple studies have found a benefit of this helpful nutrient specifically in iron overload.
“Antioxidant supplementation could reduce organ damage and premature death in patients with iron overload... We conclude that Lipoic Acid is highly effective in reversing oxidative stress arising from iron overload.” - Redox Rep. 2008;13(1):2-10.
Further research has demonstrated that Alpha Lipoic Acid improves glutathione levels and reduces iron-mediated oxidant production:
“Our results suggest Lipoic Acid may be useful in reducing complications from iron overload.” - Blood 106.11 (2005): 3599.
N-Acetyl-Cysteine (NAC)
As a precursor nutrient, NAC promotes the synthesis of glutathione in the body. Glutathione, considered by many to be the body’s most important antioxidant, works inside our cells to neutralize free radicals and reduce inflammation.
Unfortunately, many factors in our lives deplete our body’s glutathione, leading to a cycle of oxidative stress and cellular damage. Stress, genetics, environmental pollution, poor food choices, and disease can all use up the body’s glutathione reserves.
Guess what else depletes the body’s levels of glutathione? Iron!
In hemochromatosis, therefore, excess iron in the body not only causes oxidative damage by promoting free radicals, but it also works to lower one of the best defenders against the damage, glutathione. This one-two punch caused by iron may significantly contribute to the problems of hemochromatosis.
Raising glutathione levels in people with hemochromatosis has been strongly associated with better health and results. Research has shown glutathione to help reduce liver and heart damage along with improved overall antioxidant function in iron overload.
While our bodies do make their own glutathione, one of the best ways to supplement our glutathione levels is by taking NAC; a well-established precursor molecule demonstrated to boost gluathione levels in the body.
Selenium
Research demonstrates that selenium deficiency has a profound effect on iron levels, as well as other minerals. In one study, researchers found that if selenium levels are low:
- Serum iron concentration was 40-58% greater
- Transferrin saturation with iron was significantly greater (57-60% versus 30-31% with adequate selenium)
- Iron concentrations in the tissues ranged from 1.1 to 2.5 times higher
- Selenium deficiency affected the concentrations of magnesium, calcium, iron, copper, and zinc in selected tissues and serum
The researchers concluded:
“These results suggest that selenium deficiency may cause a secondary overload of iron and unbalanced distribution of other minerals.” - Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1995 Feb;59(2):302-6.
How to use Hemochromatosis Help's Milk Thistle Supreme
- For an even greater effect, Milk Thistle Supreme can be combined with Hemochromatosis Help’s Vitamin E Complete, Green Tea, Quercetin & Resveratrol, and Turmeric for the best antioxidant coverage ever created to help those with iron overload.
- Be sure to check out the Hemochromatosis Help Antioxidant Bundle and Supreme Antioxidant Bundle for more information.
- Suggested Use: 1 capsule, 2 times daily.
- Does Not Contain: Wheat, gluten, yeast, soy, animal or dairy products, fish, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, egg, ingredients derived from genetically modified organisms (GMOs), artificial colors, artificial sweeteners, or artificial preservatives.
Quality and Safety of Our Hemochromatosis Help Supplements
We have incredibly high standards when it comes to the quality and safety of nutritional supplements. We have not and will not take any shortcuts when it comes to the products available through this website!
- All of the nutritional products with our name on them are manufactured in the USA in an FDA-approved pharmaceutical-grade laboratories with verified 3rd-party testing.
- The ingredients are sourced from the best raw materials based on quality, purity, and research.
- The manufacturer has been Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) registered by the independent third-party National Sanitation Foundation (NSF International).
- Product certification ensures that what’s on the supplement label is in the bottle and that the product contains no undeclared ingredients or unsafe levels of contaminants.
- All products are manufactured in the USA in an FDA GMP compliant factory.




